Once we take into consideration bodily efficiency, we regularly think about power, velocity, or endurance. But, behind each squat, dash, or swing lies a deeper basis: motor expertise. These expertise are the constructing blocks of motion. From a child’s first steps to an elite athlete’s profitable efficiency, motor expertise decide how effectively we transfer, adapt, and excel.
On this article, we’ll discover the fundamentals of motor expertise, the distinction between advantageous vs. gross motor expertise, phases of motor improvement, and why they matter not only for athletes, however for everybody—from youngsters to older adults.
What Are Motor Expertise?
Motor expertise are discovered actions that contain the coordination of the mind, nervous system, and muscle mass to provide purposeful motion. They aren’t purely instinctive; they’re developed via repetition, apply, and neurological adaptation.
For instance:
- A toddler studying to catch a ball is growing hand-eye coordination (a motor talent).
- A weightlifter bettering squat method is refining gross motor management.
- A pianist mastering delicate finger actions is sharpening advantageous motor precision.
Motor expertise mix cognitive processes (planning the motion) and bodily execution (muscle activation). That is why they type the idea of all motion—from fundamental each day actions like strolling and consuming, to advanced athletic performances.
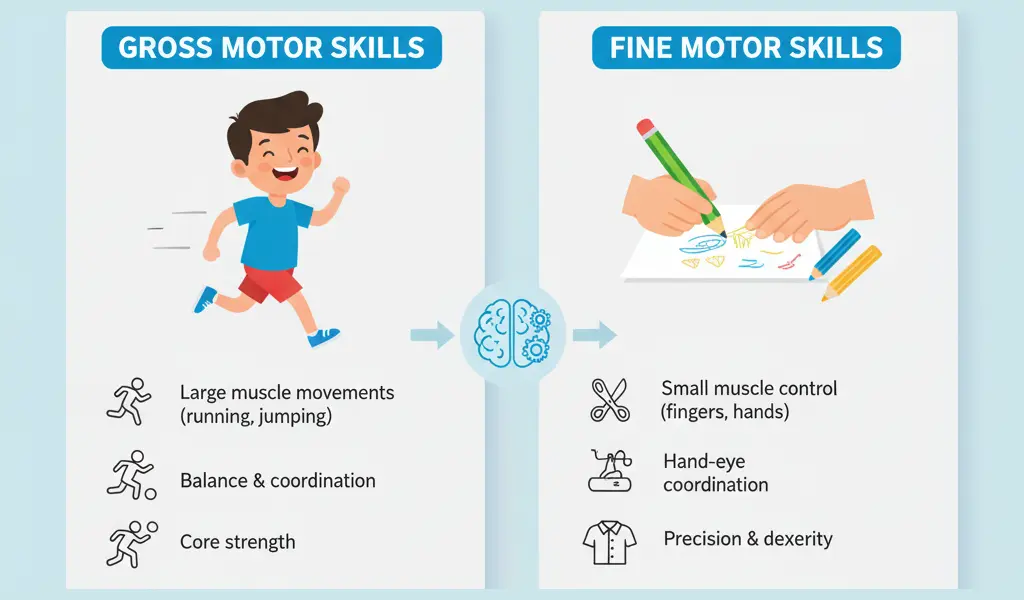
High-quality vs. Gross Motor Expertise
A central distinction in motor expertise is advantageous vs. gross motor expertise.
Gross Motor Expertise
Gross motor expertise contain massive muscle teams and whole-body actions. These expertise are important for balance, power, coordination, and mobility.
Examples embrace:
- Strolling, working, and leaping
- Throwing a ball
- Performing squats or push-ups
- Swimming strokes
Gross motor expertise are important for athletic efficiency and purposeful independence. With out well-developed gross motor coordination, even easy duties like climbing stairs or sustaining steadiness develop into difficult.
High-quality Motor Expertise
High-quality motor expertise contain smaller muscle teams—particularly within the arms, fingers, and wrists. These expertise require precision, dexterity, and management.
Examples embrace:
- Writing or drawing
- Buttoning a shirt
- Typing on a keyboard
- Controlling grip strength in sports activities (e.g., tennis, mountaineering)
High-quality motor expertise could seem much less vital for athletics, however they’re essential for sports activities requiring precision—archery, gymnastics, martial arts, and even weightlifting the place grip and bar management are important.
Levels of Motor Growth
Motor expertise develop throughout a lifelong continuum, beginning in infancy and persevering with via maturity. Understanding these phases helps trainers, coaches, and oldsters help correct development and efficiency.
1. Reflexive Actions (0–1 12 months)
- Involuntary responses to stimuli (grasp reflex, sucking reflex).
- Basis for voluntary motion.
2. Rudimentary Actions (0–2 years)
- Primary voluntary management emerges.
- Rolling, crawling, sitting, strolling.
3. Basic Motion Part (2–7 years)
- Growth of fundamental expertise: working, leaping, throwing, catching.
- Youngsters study motion patterns via play.
4. Specialised Motion Part (7–14 years)
- Expertise develop into refined and tailored for sports activities or actions.
- Transition from “play” to structured coaching.
5. Lifelong Utility (14 years onward)
- Continued refinement via apply and sport-specific coaching.
- Adults adapt motor expertise to non-public targets (athletics, health, or each day operate).
- Later in life, motor talent upkeep is essential for independence and fall prevention.
Why Motor Expertise Matter
Motor expertise should not only for youngsters or athletes—they’re important throughout the human lifespan. Right here’s why they matter:
1. Athletic Efficiency
- Coordination and effectivity: Athletes with higher motor expertise use much less power for actions.
- Response time: Fast motor responses decide success in aggressive environments.
- Talent acquisition: From dribbling a basketball to performing Olympic lifts, all athletic expertise stem from motor studying.
2. Every day Perform
- Easy actions—tying footwear, driving, carrying groceries—depend on motor expertise.
- Robust motor expertise enhance independence and confidence in on a regular basis life.
3. Damage Prevention
- Poor motor management typically results in motion compensations.
- Correct coordination and stability decrease the danger of overuse accidents and falls.
4. Cognitive Well being
- Motor expertise and cognitive processes are tightly linked.
- Analysis exhibits that studying new motor expertise enhances mind plasticity, bettering reminiscence and problem-solving.
5. Getting older and Longevity
- Motor talent coaching preserves mobility, coordination, and steadiness in older adults.
- Prevents falls, one of many main causes of damage in getting older populations.
How Motor Expertise Are Realized: The Science of Motor Studying
Motor talent acquisition entails each the mind and the physique.
Key Parts:
- Neuroplasticity: The mind adapts by creating stronger neural pathways with apply.
- Suggestions: Exterior suggestions (from coaches or know-how) accelerates studying.
- Levels of studying: Cognitive (understanding the duty), associative (refining), autonomous (computerized execution).
- Repetition with variation: Repeating a talent below completely different situations enhances adaptability.
Athletes and coaches use motor studying ideas to design coaching classes that enhance coordination, effectivity, and flexibility.
Workout routines to Enhance Motor Expertise
Motor expertise can all the time be developed—whether or not you’re a toddler, grownup, athlete, or older grownup.
Gross Motor Talent Workout routines
- Agility ladders (footwork, coordination)
- Dash drills (response time, velocity)
- Steadiness board coaching (stability, proprioception)
- Energy coaching with free weights (whole-body coordination)
High-quality Motor Talent Workout routines
- Grip strengtheners (hand coordination, dexterity)
- Ball toss-and-catch drills with small objects
- Finger dexterity workouts (piano, typing, or remedy putty)
- Precision sports activities apply (archery, darts, desk tennis)
For Older Adults
- Tai chi (steadiness, managed motion)
- Strolling with various surfaces (coordination)
- Gentle resistance coaching (motor recruitment)
- Useful duties (carrying, reaching, bending)
Motor Expertise in Sports activities
Athletes typically distinguish themselves by their mastery of motor expertise:
- Basketball: Dribbling requires advantageous motor management of the fingers and gross motor coordination for agility.
- Soccer: Ball dealing with, steadiness, and agility depend on exact motor expertise.
- Gymnastics: Combines advantageous management (grip, steadiness) with gross motor acrobatics.
- Weightlifting: Excellent timing and coordination of a number of joints is crucial.
Even inside the similar sport, athletes with superior motor management typically excel sooner and carry out extra constantly below strain.
Bettering Motor Expertise Via Coaching
For coaches, trainers, or people, listed below are evidence-based suggestions:
- Prioritize method over load – Energy with out coordination results in poor motor improvement.
- Incorporate variability – Observe expertise in several contexts (e.g., dribbling on completely different surfaces).
- Use suggestions loops – Video evaluation, coach corrections, or wearable know-how assist refine actions.
- Progress regularly – Transfer from fundamental to advanced duties.
- Combine cognitive challenges – Twin-task coaching (motion + psychological duties) improves each mind and motor operate.
Conclusion
Motor expertise are the basis of all motion—from on a regular basis actions to elite sports activities efficiency. Understanding the distinction between advantageous vs. gross motor expertise, recognizing their phases of improvement, and coaching them strategically can improve efficiency, enhance well being, and promote lifelong independence.
Whether or not you’re an athlete searching for peak efficiency, a guardian supporting baby improvement, or an older grownup aiming to remain lively and balanced, motor expertise are central to your journey. By investing in motion expertise and bodily coordination, you’re not simply coaching your physique—you’re coaching your mind, your resilience, and your long-term well-being.
References
- Gallahue, D. L., Ozmun, J. C., & Goodway, J. D. (2012). Understanding Motor Growth: Infants, Youngsters, Adolescents, Adults (seventh ed.). McGraw-Hill.
- Payne, V. G., & Isaacs, L. D. (2017). Human Motor Growth: A Lifespan Method (ninth ed.). Routledge.
- Schmidt, R. A., & Lee, T. D. (2019). Motor Studying and Efficiency: From Ideas to Utility (sixth ed.). Human Kinetics.
- Haywood, Ok. M., & Getchell, N. (2020). Life Span Motor Growth (seventh ed.). Human Kinetics.
- Clark, J. E., & Metcalfe, J. S. (2002). The mountain of motor improvement: A metaphor. In J. E. Clark & J. H. Humphrey (Eds.), Motor Growth: Analysis and Evaluations (Vol. 2, pp. 163–190). NASPE Publications.
- Adolph, Ok. E., & Robinson, S. R. (2015). The highway to strolling: What studying to stroll tells us about improvement. In A. Slater & P. C. Quinn (Eds.), Developmental Psychology: Revisiting the Basic Research (pp. 102–120). SAGE Publications.
- Barnett, L. M., et al. (2009). Childhood motor talent proficiency as a predictor of adolescent bodily exercise. Journal of Science and Medication in Sport, 19(3), 267–272.
- Williams, H. G., Pfeiffer, Ok. A., O’Neill, J. R., Dowda, M., McIver, Ok. L., Brown, W. H., & Pate, R. R. (2008). Motor talent efficiency and bodily exercise in preschool youngsters. Weight problems, 16(6), 1421–1426.
- Voelcker-Rehage, C., & Niemann, C. (2013). Structural and purposeful mind modifications associated to several types of bodily exercise throughout the life span. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Evaluations, 37(9), 2268–2295.
- World Health Organization (2019). Tips on Bodily Exercise, Sedentary Behaviour and Sleep for Youngsters Underneath 5 Years of Age. Geneva: WHO.