Enrollment in Medicare Benefit, the personal plan different to conventional Medicare, has elevated steadily over the previous 20 years, and since 2023, more than half of eligible beneficiaries have enrolled in Medicare Benefit. Amidst this progress, an rising variety of beneficiaries are enrolling in particular wants plans (SNPs), particularly since 2018, when SNPs grew to become a everlasting a part of the Medicare Benefit program. SNPs now account for 21% of all Medicare Benefit enrollees, in contrast with simply 13% in 2018. The rise within the share of Medicare Benefit enrollees in SNPs additionally implies that SNPs contribute disproportionately to the expansion in Medicare Benefit enrollment. For instance, between 2024 and 2025, progress in SNPs comprised nearly half (48%) of the entire enhance in Medicare Benefit enrollment.
There are three varieties of SNPs, and enrollment in every is restricted to particular teams of beneficiaries, all of which comprise a number of the highest-need beneficiaries within the Medicare inhabitants. Over 4 in 5 (82%) SNP enrollees are enrolled in twin eligible SNPs (D-SNPs), that are restricted to folks with each Medicare and Medicaid (“dual-eligible individuals”). Dual-eligible individuals are likely to have decrease incomes, extra continual situations, and extra practical and cognitive impairments than Medicare beneficiaries with out Medicaid protection. The 2 different varieties of SNPs are continual situation SNPs (C-SNPs, 16% of enrollees), that are restricted to folks with sure continual situations, and institutional SNPs (I-SNPs, 2% of enrollees), that are restricted to individuals who require an institutional degree of care. All SNPs are required to have a mannequin of care, or framework detailing how the plan will determine the wants of every enrollee and tackle these wants by means of the plan’s care administration practices. Different necessities differ throughout the three varieties of SNPs. D-SNPs might have further necessities relying on the state by which they function. (See Field 1 for added info.)
In recent times, the Facilities for Medicare and Medicaid Providers (CMS) has made a number of adjustments to necessities for D-SNPs and different Medicare Benefit plans, which can have an effect on insurer selections concerning the varieties of plans they provide and promote. To higher perceive the rising function of SNPs in Medicare Benefit and the potential implications for beneficiaries of adjustments to SNP and Medicare Benefit plan necessities, this temporary examines SNP enrollment patterns and developments utilizing current Medicare Benefit enrollment knowledge printed by CMS.
Key Takeaways
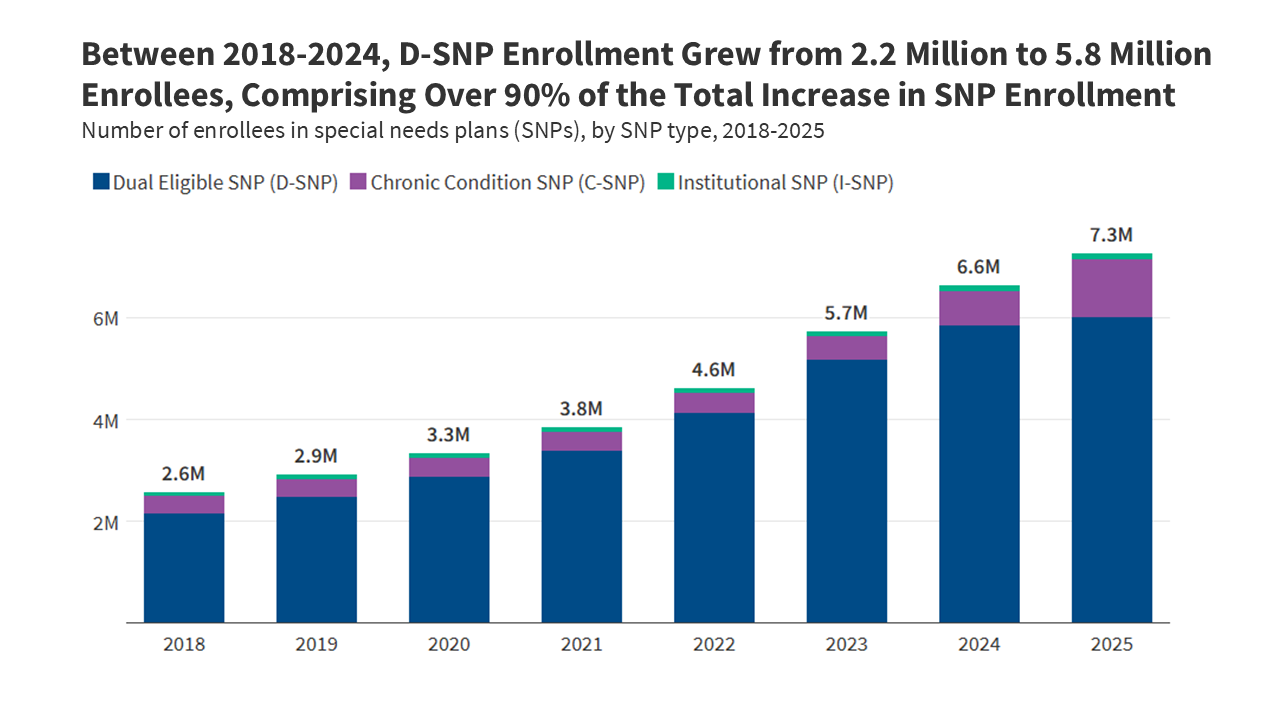
- Since 2018 when SNPs grew to become a everlasting a part of the Medicare program, SNP enrollment has tripled, rising from 2.6 million to 7.3 million, a rise of practically 4.7 million enrollees.
- By 2024, progress in SNPs was pushed by a rise in enrollment in D-SNPs, which grew from 2.2 million enrollees in 2018 to five.8 million enrollees in 2024, comprising greater than 90% of SNP enrollment progress over that point.
- C-SNPs comprised 75% of whole SNP enrollment progress between 2024 and 2025, in distinction to prior years, the place enrollment progress was primarily in D-SNPs. In 2025, C-SNP enrollment elevated by 476,300 new enrollees, triple the rise in D-SNP enrollment (159,400 new enrollees).
- A small share of SNP enrollees, simply 14%, are in plans administered by non-profit insurers. SNP enrollment is extremely concentrated amongst a small variety of massive nationwide carriers, with UnitedHealth Group and Humana plans comprising over half (54%) of whole SNP enrollment. UnitedHealth Group accounts for half of all C-SNP enrollees.
- The acceleration of C-SNP enrollment progress and slowing of D-SNP enrollment progress coincided with implementation of recent guidelines for D-SNPs requiring better integration between Medicare and Medicaid. C-SNPs usually are not required to have the same degree of integration.
From 2018-2024, progress in SNP enrollment was pushed by will increase in D-SNP enrollment, plans for dual-eligible people.
From 2018, when SNPs grew to become a everlasting a part of the Medicare Benefit program, by means of 2024, progress in SNP enrollment was predominantly as a result of progress in enrollment in D-SNPs. In 2018, 2.2 million folks had been enrolled in a D-SNP, and in 2024, 5.8 million folks had been enrolled in a D-SNP. That enhance includes greater than 90% of the entire enhance in SNP enrollment between 2018 and 2024.
C-SNP enrollment and I-SNP enrollment additionally elevated throughout this era, although on a smaller scale relative to D-SNP enrollment progress. C-SNP enrollment grew from 346,000 enrollees in 2018 to 674,500 enrollees in 2024, and I-SNP enrollment grew from 71,500 enrollees in 2018 to 115,100 enrollees in 2024.
SNPs obtain higher per capita payments underneath the Medicare Benefit fee system, on common, as a result of enrollees have greater anticipated spending as a result of their greater well being care wants. It’s well-documented, nevertheless, that Medicare Benefit pays extra for Medicare Benefit enrollees than spending can be for a similar folks in the event that they had been coated underneath conventional Medicare, and in 2025, MedPAC estimates that funds had been 20% greater, on common. The upper funds are largely pushed by the danger adjustment system, which pays extra for people who find themselves sicker, and fewer for individuals who are more healthy, relying closely on recognized heath situations to find out changes to fee based mostly on well being standing. SNPs are doubtlessly higher positioned to leverage this method to extend their funds relative to enrollee’s prices, contributing to greater margins for SNPs, on common, than different Medicare Benefit plans. MedPAC discovered that in 2022, the typical margins for D-SNPs (7.5%) and C-SNPs (7.4%) had been double the typical margins of Medicare Benefit plans total (3.6%). In flip, these greater funds depart more resources for plans to supply supplemental benefits that enchantment to a inhabitants with advanced well being care wants.
Enrollment progress in SNPs from 2024-2025 was pushed by a rise in enrollment in C-SNPs, plans for folks with continual situations.
In recent times, CMS has made a number of adjustments to necessities for Medicare Benefit plans typically out there to the general public and D-SNPs, however not C-SNPs, which can have an effect on insurer selections about what varieties of plans to supply. Beginning in 2022, CMS now not contracts with typical Medicare Benefit plans that enroll a minimum of 80% dual-eligible people (“D-SNP look-alikes”). In 2025, this threshold was lowered to 70% and is scheduled to be lowered to 60% beginning in 2026. Moreover, starting in 2025, totally built-in twin eligible (FIDE) SNPs and extremely built-in twin eligible (HIDE) SNPs have new enrollment, profit, and coordination necessities (see Field 1 for added particulars). The extra necessities are supposed to advertise higher integration between Medicare and Medicaid for enrollees however may make D-SNPs much less engaging to personal insurers. These requirement adjustments may incentivize efforts to enroll extra dual-eligible people in C-SNPs, which aren’t topic to the look-alike thresholds like typical Medicare Benefit plans or Medicaid integration and coordination necessities like D-SNPs, notably since many dual-eligible people have chronic conditions that will qualify them for C-SNP enrollment.
In distinction to earlier years when enrollment progress in SNPs was pushed by elevated enrollment in D-SNPs, the biggest enhance in enrollment in SNPs from 2024 to 2025 was in C-SNPs, comprising greater than three-quarters of the change in total SNP enrollment. C-SNP enrollment elevated sharply, rising by 476,300 enrollees from 2024 to 2025. That interprets right into a 71% soar over a one-year interval. D-SNP enrollment and I-SNP enrollment remained comparatively steady over the identical interval, with D-SNP enrollment rising by solely 3% (159,400 enrollees) and I-SNP enrollment staying basically unchanged.
Whereas C-SNP enrollment has elevated extra shortly for the reason that D-SNP look-alike guidelines first went into impact in 2022, the change accelerated during the last 12 months, as the principles tightened additional and different Medicaid integration and coordination necessities for FIDE and HIDE SNPs went into impact. That is the primary time that the variety of further C-SNP enrollees has surpassed the variety of further D-SNP enrollees. A current analysis of 2025 enrollment knowledge (not but out there to KFF) reveals that by means of January of 2025, just below 20% of the rise in C-SNP enrollment was comprised of dual-eligible people.
Twin-eligible people comprised a bigger share of enrollment in SNPs than in non-SNP Medicare Benefit plans. For instance, in 2023, 93% of SNP enrollees had been dual-eligible people, which aligns with the dominance of D-SNPs within the SNP market. Over 90% of I-SNP enrollees had been additionally dual-eligible people in 2023, reflecting the truth that Medicaid is the first payer of long-term care, so folks counting on an institutional degree of care usually tend to be enrolled in each Medicare and Medicaid. In 2023, 1 / 4 of enrollees in C-SNPs had been dual-eligible people, whereas 9% of enrollees in particular person Medicare Benefit plans had been dual-eligible people.
For all SNP varieties, enrollment is extremely concentrated amongst a small variety of massive nationwide carriers.
Throughout all three SNP varieties, which enroll a number of the most susceptible beneficiaries within the Medicare inhabitants, just a few massive nationwide carriers account for bigger shares of enrollment within the SNP market as in contrast with the general Medicare Benefit market. The distribution of D-SNP enrollment by insurer is extra closely concentrated in UnitedHealth Group Inc. (38% vs 29%) and Elevance Well being Inc. (10% vs 7%) than for the general Medicare Benefit market. UnitedHealth Group Inc. accounts for half (51%) of all C-SNP enrollment. Extra companies comprising bigger shares of enrollment in C-SNPs than within the total Medicare Benefit market embody Humana Inc. (20% vs 17%) and Elevance Well being Inc. (12% vs 7%). Though UnitedHealth Group Inc. accounts for a majority (51%) of I-SNP enrollment in 2025, smaller insurers play a bigger function within the I-SNP market than within the total Medicare Benefit market (42% vs 33%). General, 14% of SNP enrollees are in a plan provided by a non-profit group (16% of D-SNP enrollees, 3% of C-SNP enrollees, and 5% of I-SNP enrollees).
For dual-eligible people, D-SNPs provide extra integration with Medicaid than C-SNPs.
To facilitate integration of Medicare and Medicaid protection, D-SNPs are required to contract with state Medicaid businesses, whereas C-SNPs usually are not topic to further integration necessities. The minimal D-SNP necessities, that are set on the federal degree, differ throughout the three classes of D-SNPs and may change year-to-year throughout annual rule making. D-SNPs with greater ranges of integration, HIDE and FIDE SNPs, have further necessities (see Field 1 for extra particulars). Moreover, D-SNPs may be designated as relevant built-in plans in the event that they meet federal necessities, together with solely aligned enrollment, protecting a minimum of some Medicaid providers by means of the D-SNP or an affiliated Medicaid managed care plan, and a unified grievance and appeals system. Given the dearth of C-SNP integration necessities, to the extent the acceleration in C-SNP enrollment was pushed by dual-eligible people, efforts to encourage better integration between Medicare and Medicaid might face challenges.
States might set up further necessities for D-SNPs by means of their contracts. Responses from KFF’s 24th annual price range survey of Medicaid officers in all 50 states and the District of Columbia in July 2024 present that these necessities differ throughout the various kinds of D-SNPs. For instance, simply over half (19) of the 35 states with coordination-only D-SNPs required these plans to incorporate any of the extra elective necessities, the most typical of which was providing sure supplemental advantages (7 states) and offering built-in member supplies, resembling one abstract of advantages doc that gives info on advantages coated by each Medicare and Medicaid (5 states). HIDE and FIDE SNPs operated in lower than half of states in 2024, although most states had further necessities for most of these plans past the federal necessities (14 of 15 for HIDE SNPs and all 12 states for FIDE SNPs) (Determine 4). New federal necessities for HIDE and FIDE SNPs went into impact in 2025. For FIDE SNPs, these embody solely aligned enrollment, which limits enrollment to full-benefit dual-eligible people who had been enrolled within the affiliated Medicaid managed care plan, and the requirement that the affiliated plan cowl behavioral health, and sure different Medicaid advantages. To the extent these weren’t beforehand required by states, the brand new necessities might characterize a further burden for Medicare Benefit insurers and will affect their selections on which plans to supply. In 2024, most states with FIDE SNPs did have these necessities. Particularly, of the 12 states with FIDE SNPs, 9 required solely aligned enrollment and 10 required the affiliated Medicaid managed care plan to cowl behavioral well being. (New necessities for HIDE SNPs weren’t among the many gadgets requested within the price range survey.) Whereas these necessities are supposed to facilitate integration and coordination between the applications, the comparatively low availability of HIDE and FIDE SNPs might restrict how efficient they’re at reaching that objective.
Field 1. Sorts of Particular Wants Plans
Twin Eligible Particular Wants Plans
Twin eligible particular wants plans (D-SNPs) are restricted to people who find themselves enrolled in each Medicare and Medicaid. There are three varieties of D-SNPs:
Coordination-only Twin Eligible Particular Wants Plans: Any such D-SNP offers Medicare-covered providers and is required to coordinate the supply of advantages with the Medicaid program, contract with state Medicaid applications, and notify states when enrollees are admitted to an inpatient hospital or expert nursing facility.
Extremely Built-in Twin Eligible Particular Wants Plans: Any such D-SNP should meet the necessities of coordination-only D-SNPs (besides the notification necessities) and should additionally embody protection of long-term care, behavioral well being, or each.
New for 2025: HIDE SNPs will need to have aligned service areas, which means they need to even have a Medicaid plan working in the identical counties because the D-SNP.
Absolutely Built-in Twin Eligible Particular Wants Plans: Any such D-SNP should meet the necessities of coordination-only D-SNPs (besides the notification necessities) and supply Medicare and included Medicaid coated providers by means of a single managed care group. The identical group that provides the FIDE SNP should additionally provide a Medicaid managed care plan for any Medicaid advantages not included within the FIDE SNP. In some circumstances, sure Medicaid advantages could also be supplied by the state or by a distinct well being plan. FIDE SNPs are paid by Medicare for Medicare-covered providers and supplemental advantages included within the plan, and by Medicaid for Medicaid-covered providers.
New for 2025: FIDE SNPs will need to have exclusively aligned enrollment, which means they might solely enroll full-benefit dual-eligible people who’re enrolled in each the FIDE SNP and the Medicaid plan sponsored by the identical group, and both the D-SNP or Medicaid plan should cowl long-term care and all Medicaid advantages through a separate capitated fee association.
Power Situation Particular Wants Plans
Power situation particular wants plans enroll people who’ve particular extreme or continual disabling situations. Almost all (97%) C-SNPs plans are for folks with diabetes or cardiovascular situations.
Institutional Particular Wants Plans
Institutional particular wants plans enroll people who want providers to be supplied in a long-term care facility for a minimum of 90 days.
Strategies
Information: SNP enrollment knowledge are from the Particular Wants Plan (SNP) knowledge printed by Facilities for Medicare & Medicaid Providers (CMS) within the Medicare Benefit (MA)/Half D Contract and Enrollment Information part in March of the respective 12 months. Enrollment knowledge are solely supplied for plan-county mixtures which have a minimum of 11 beneficiaries; thus, we exclude any plans that don’t meet this enrollment threshold.
This evaluation makes use of knowledge from the CMS Medicare Benefit Profit and Panorama recordsdata for the respective 12 months. Medicare Benefit enrollment and dual-eligible beneficiary enrollment are based mostly on evaluation of the Facilities for Medicare & Medicaid Providers (CMS) Power Situations Information Warehouse (CCW) research-identifiable Grasp Beneficiary Abstract File (MBSF) Base in 2023.
Figuring out dual-eligible enrollees as a share of SNP enrollees: Beneficiaries with a legitimate contract ID and plan ID in March 2023 had been recognized as enrolled in Medicare Benefit. To find out the kind of plan by which the beneficiary was enrolled, the contract ID and plan ID had been matched to the March 2023 Month-to-month Enrollment by Plan, or the Particular Wants Plan Report knowledge printed by CMS. This consists of enrollment in all personal plans that are predominately Medicare Benefit plans.
Counts of dual-eligible people embody each full-benefit and partial-benefit dual-eligible people. Twin standing in March (03) 2023 was recognized utilizing the Medicare month-to-month twin standing code DUAL_STUS_CD_03 with values of 01,02,03,04,05,06, or 08. Enrollees additionally needed to have each Half A and B in March 2023 to be included on this evaluation. We excluded enrollees from Puerto Rico and the Virgin Islands from this evaluation.
This work was supported partially by Arnold Ventures. KFF maintains full editorial management over all of its coverage evaluation, polling, and journalism actions.