On July 4, President Trump signed into law a funds and tax invoice that features significant changes to the Medicaid program together with new necessities for states to implement work requirements for people enrolled by way of the Inexpensive Care Act (ACA) Medicaid growth pathway or sure state waivers. The Congressional Finances Workplace (CBO) estimates that this requirement may have the largest effect on spending and protection in comparison with different provisions, decreasing federal Medicaid spending by $326 billion over ten years and leading to 5.3 million extra people who find themselves uninsured.
In the summertime of 2025 whereas the brand new legislation was below debate in Congress and shortly after enactment, the 25th annual funds survey of Medicaid officers in all 50 states and the District of Columbia performed by KFF and Well being Administration Associates (HMA), in collaboration with the Nationwide Affiliation of Medicaid Administrators (NAMD) was within the subject. To higher perceive how states are making ready for Medicaid work necessities, the survey requested states to debate anticipated challenges to implementing work necessities by the top of 2026, together with associated system adjustments and information matching. KFF anticipates that work necessities will apply to 43 states (41 growth states together with the District of Columbia plus Georgia and Wisconsin, which have expanded Medicaid by way of waivers). We acquired responses to this query from 42 of those states.
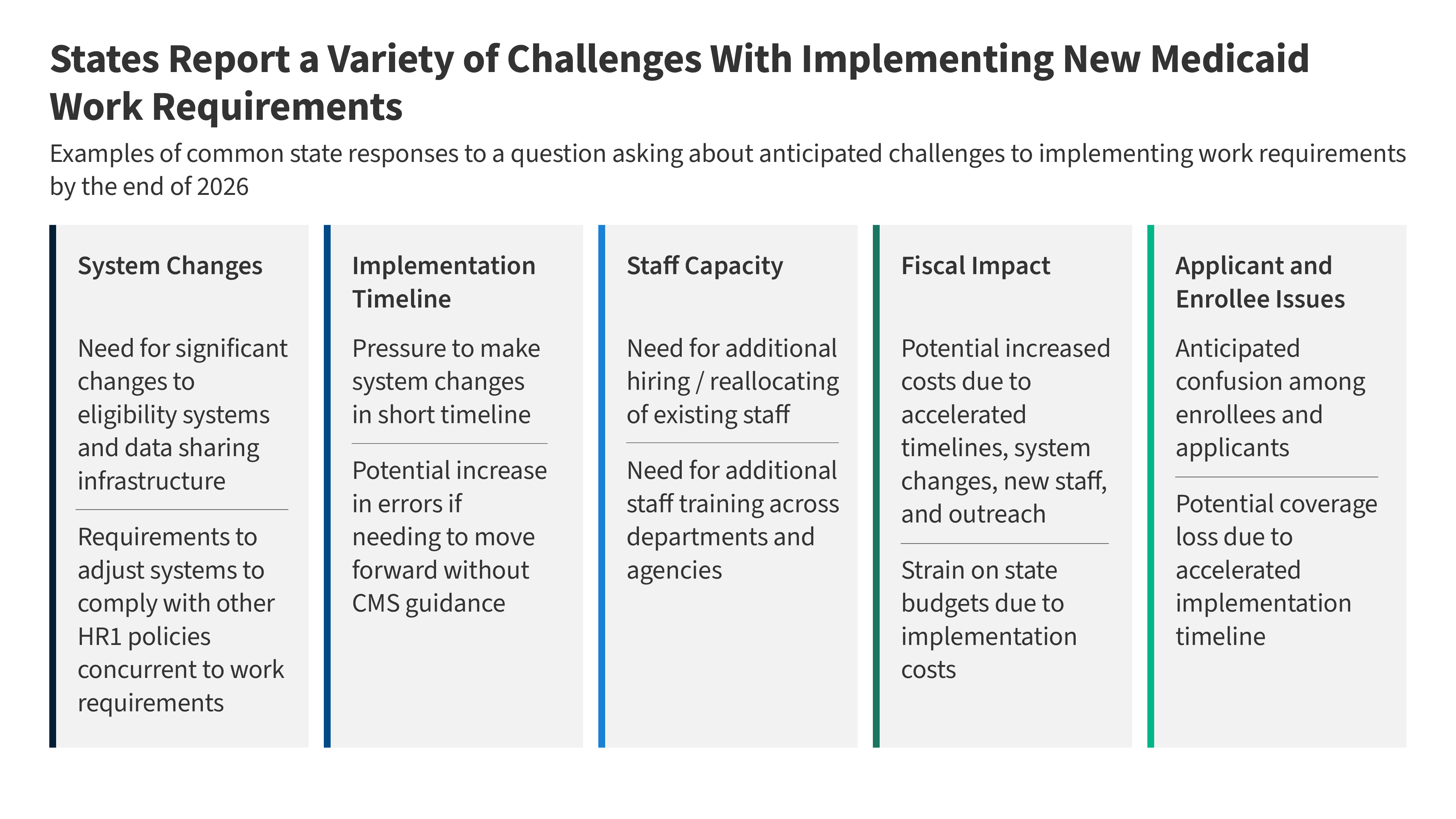
As a result of the survey query requested particularly about challenges pertaining to techniques, almost all states described system adjustments they anticipate to make; nonetheless, they recognized different challenges as effectively. These challenges embrace how rapidly the necessities should be applied, employees capability issues, value issues, and points for candidates and enrollees (Determine 1). In lots of instances, states described a number of, interrelated challenges. For instance, the compressed implementation timeframe and want for federal steering usually factored into state responses detailing different challenges. Some states expressed extra challenges than others. Just a few states that had already been pursuing 1115 waivers to implement work necessities reported fewer anticipated implementation challenges. Understanding state challenges will help inform the content material and timing of forthcoming federal steering.
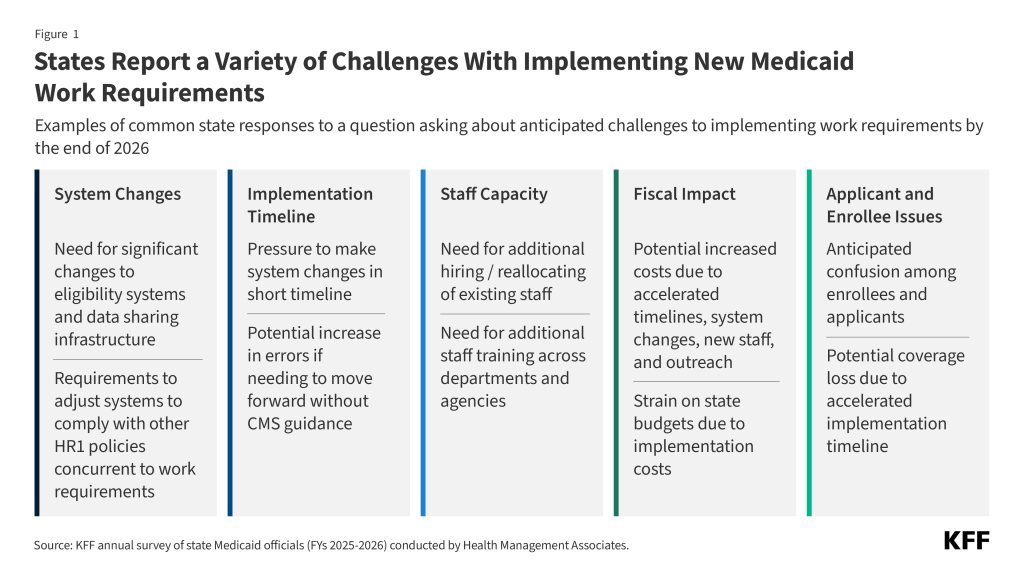
States cited the necessity to make main adjustments to eligibility techniques in a brief timeframe and the necessity for enhanced information sharing infrastructure as main challenges. States might want to make important adjustments to eligibility techniques to have the ability to confirm compliance with work, college, and different qualifying actions in addition to to determine people who qualify for obligatory exemptions and optionally available exceptions. States expressed concern over having to make such main system adjustments in a really brief timeframe, noting the lengthy lead occasions usually wanted to design, procure, and construct new techniques. Including to the problem would be the have to make key system design and workflow selections earlier than CMS releases steering. One other precedence many states talked about is enhancing capabilities to gather and match information from a number of businesses and exterior sources (e.g., SNAP, Medicaid claims information, state training enrollment information) to scale back the burden on candidates and enrollees for documenting their work or exemption standing (Determine 2). Nevertheless, some states acknowledged that information sharing infrastructure is restricted and establishing interfaces to precisely share information will take time to place in place.
In accordance with a number of states, other policy changes within the legislation, together with restrictions on eligibility for lawfully current immigrants, 6-month eligibility redeterminations for growth enrollees, and limits to retroactive Medicaid protection, additionally require important techniques adjustments. Rising this complexity, some states additionally talked about the problem of aligning totally different work necessities throughout Medicaid, SNAP, and TANF, in addition to having to make advanced techniques and eligibility coverage adjustments for SNAP as required by the brand new legislation. These adjustments could also be significantly sophisticated for states with built-in Medicaid and SNAP eligibility techniques. As well as, a number of states famous that they’re at present concerned in multiyear IT techniques initiatives and that it will likely be difficult to finish these initiatives efficiently whereas additionally concurrently including new techniques redesigns. All of those techniques challenges are additional exacerbated by restricted state employees capability and monetary assets.
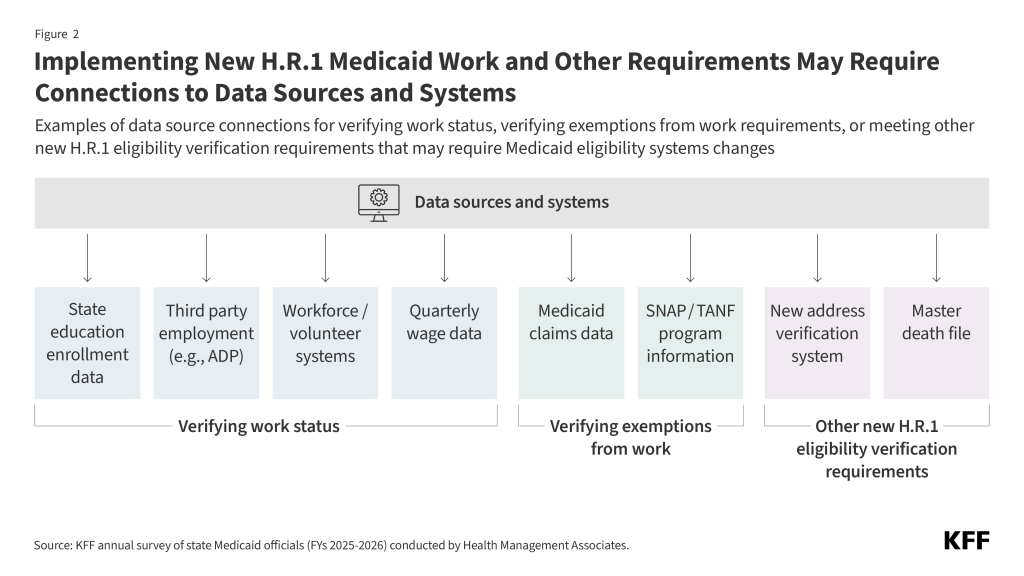
In accordance with many states, the brief implementation timeline means they might want to transfer rapidly with key techniques adjustments and coverage selections earlier than clear federal steering is accessible. States have simply over a 12 months to organize to implement work necessities on January 1, 2027, and have lower than a 12 months earlier than they might want to start outreach to inform people of the brand new necessities in September 2026 (Determine 3). The legislation directs the Secretary of HHS to situation an interim closing rule on implementing work necessities by June 1, 2026, leaving little time between when the steering is launched and when outreach begins. For a lot of states, this brief timeline intensifies the stress to maneuver rapidly with system upgrades, significantly given the usually prolonged vendor procurement course of, and different key selections. Nevertheless, a number of states emphasised the dangers of shifting ahead within the absence of clear steering, noting that if state selections are usually not aligned with the federal expectations, the ensuing rework would enhance prices and probably delay assembly vital deadlines. Some states described the implementation deadline as unrealistic, noting that it will increase the chance of errors that would result in pointless protection losses. In gentle of those dangers, some states stated early and clear steering from CMS can be useful, particularly on points such because the definition of medical frailty and different exemptions or the permissibility of self-attestation that would have an effect on techniques selections.
A small variety of states explicitly talked about curiosity within the choice for states to pursue good religion waivers to delay implementation of labor necessities, noting that further steering can be wanted to know the factors to acquire a “good religion waiver” and the state utility course of.
Determine 3
A number of states reported workforce challenges, together with the necessity to rent or reallocate employees in anticipation of elevated workloads and the necessity for extra employees coaching. Many states reported that they might want to rent further employees or reallocate present employees to deal with elevated workloads from verifications, appeals, and enrollee outreach. States additionally anticipate the necessity for extra employees coaching, together with coaching employees throughout departments and businesses (e.g., SNAP), to make sure eligibility staff perceive the brand new guidelines and necessities, exemption standards, and documentation necessities. Just a few states referred to as out the extra workforce assets that shall be essential to conduct complete and multi-modal outreach efforts and reply to the anticipated enhance in enrollee inquiries.
Just a few states famous that employees are already managing main multiyear initiatives which can be underway, akin to eligibility system modernization initiatives, forcing employees and management to juggle competing calls for. Equally, restricted employees capability may trigger spillover results and end in much less well timed eligibility determinations for enrollees not topic to work necessities.
Even with implementation funds and federal matching funds for administrative prices, some states cited the elevated prices of implementing work necessities as a priority. Various states explicitly talked about the fiscal implications tied to techniques adjustments, hiring further employees, and conducting outreach to enrollees. One state famous that, given the tight timeframe coupled with the enormity and complexity of the brand new necessities tied to system adjustments, interagency agreements, state rulemaking, and enrollee outreach, states may have to maneuver ahead on a number of parallel tracks, which may enhance implementation prices and the chance for errors. Contracts for techniques adjustments or new parts are pricey, and states famous that accelerated timelines usually enhance these prices. Some states additionally reported that the elevated prices will additional pressure already constrained state budgets. As well as, some states mentioned that new monetary penalties for error charges in SNAP and Medicaid could probably have an effect on how they transfer ahead with system adjustments. The brand new legislation supplies $200 million in funding to states for techniques improvement, with states capable of entry federal matching funds. The federal authorities generally provides 50 % of the funds for administrative actions however pays for as much as 90 % of sure administrative prices, together with for sure IT system adjustments.
Whereas not requested immediately about enrollee points, a number of states cited issues for candidates and enrollees, together with anticipated confusion over the brand new necessities and attainable protection losses. States anticipate confusion amongst enrollees and candidates in regards to the new work necessities and listed educating people among the many challenges they’ll face. Whereas states famous the significance of outreach to shoppers, a number of reported that efforts to maneuver ahead with communication and outreach with out federal steering may end in extra enrollee confusion if CMS steering doesn’t align with state assumptions associated to documentation necessities, exemption definitions, or information matching. Some states additionally expressed concern over attainable protection loss stemming from the accelerated implementation timeline and indicated that they plan to analyze methods they will reduce any protection losses. One state famous explicit issues for enrollees in rural areas with restricted web entry and people with jobs with fluctuating work hours.